You are here
A comfortable home that respects the environment

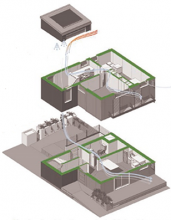
The domestic greywater reuse system implemented in the Sustainable Social Housing project at the CTEC Park in Pudahuel allows the electrochemical and membrane technologies developed in the research to be applied to filter water from showers, sinks, washing machines, and kitchen sinks for reuse.
One such use is irrigating the plants that cover the walls and green roofs of the housing, providing a sustainable solution that improves the building's thermal and acoustic insulation. This method enables the recycling of 65% of drinking water for non-consumption purposes.
Construction and Equipment:
Beyond the indisputable importance of gray water reuse, however, the property incorporates a number of other technologies to protect the environment, provide comfort to its inhabitants, and reduce the cost of basic services.
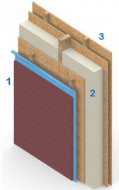
According to the Ministry of Housing and Urban Development's (Minvu) Housing Energy Rating System (CEV), this 55 m² two-story house is considered energy efficient. The construction of its walls stands out in particular. They are made of panels (see Box 1) that provide significant thermal insulation due to the attributes of their materials and the use of insulated air chambers. Additionally, all the windows are made of PVC thermopanels.
Additionally, the house has an innovative heat dissipation system that uses cross ventilation through a convective evaporative tower. Hot air enters through the upper floor and is humidified by humidifiers. It then descends through the interior of the tower and is expelled through the first-floor windows (see Box 2).
Electricity Supply
This prototype house has an autonomous electricity supply thanks to a 2 kW photovoltaic system consisting of four panels. The system is "on-grid," meaning it is connected to the electricity supply network. This allows the system to draw the necessary differential when energy requirements exceed its generation capacity. Hot water is provided by two heaters: a 150-liter solar heater and an 80-liter electric heater.
Due to the combination of installed technologies, energy consumption for heating can be reduced by 58%, and energy consumption for cooling can be reduced by 43%.
Some of its features:
The Usach Faculty of Technology created Sustainable Social Housing as a project to participate in "Construye Solar 2019," an initiative in which different universities presented prototypes of social housing. Their performance in terms of water and energy efficiency was then measured. The Usach project won first place in the categories of innovation, water efficiency, well-being and comfort, housing performance, communication, and social awareness.
The 22-centimeter-thick walls consist of panels with an exterior ventilated chamber (1) filled with blown cellulose (2), as well as an airtight interior chamber (3).
The house is cooled by the evaporative tower and cross ventilation. Hot air enters through the top, where it is humidified and cooled by humidifiers. The air then descends and is expelled outside through the ground-floor windows.
Thermal imaging cameras were used to evaluate the building's performance and check the thermal insulation and cooling.
News
 A successful seminar was held on advanced gray water treatment and...
A successful seminar was held on advanced gray water treatment and...
 The international academic network will present its advances in gray...
The international academic network will present its advances in gray...
 The GWR Project attended the Chemical Engineering Congress.
The GWR Project attended the Chemical Engineering Congress.